lv remodelling | concentric remodeling and hyperdynamic systolicfunction lv remodelling Many factors influence the time course and extent of remodeling, including the severity of the injury, secondary events (recurrent ischemia . See more
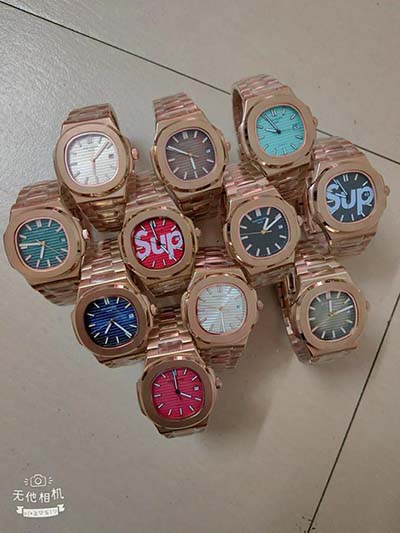
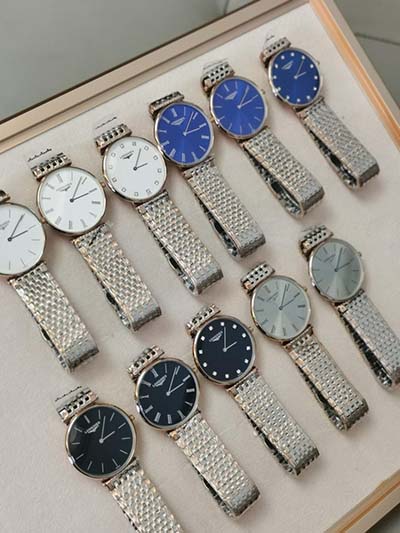
The entry-point — Rolex Oyster Perpetual Date ref. 1500. Last week, I actually picked a Datejust as the entry-point. In the 1960s, Rolex introduced the famous Datejust 1600-series with the updated Caliber 1565. It’s a seriously great option if you want to buy a great vintage Rolex as is the Rolex Air-King.
0 · ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction
1 · left ventricular remodeling process
2 · drugs that prevent cardiac remodeling
3 · concentric remodeling vs hypertrophy
4 · concentric remodeling should i exercise
5 · concentric remodeling and hyperdynamic systolicfunction
6 · concentric left ventricular remodeling treatment
7 · concentric left ventricular remodeling causes
May 4, 1970 - Four students from Kent State University in Ohio were killed and nine wounded by National Guardsmen during a protest against the Vietnam War spread into Cambodia. August 12, 1970 - The United .
In cardiology, ventricular remodeling (or cardiac remodeling) refers to changes in the size, shape, structure, and function of the heart. This can happen as a result of exercise (physiological remodeling) or after injury to the heart muscle (pathological remodeling). The injury is typically due to acute myocardial . See moreThe cardiac myocyte is the major cell involved in remodeling. Fibroblasts, collagen, the interstitium, and the coronary vessels to . See more• Anatomy portal• Dor procedure• Athlete's heart See more• "Left Ventricular Remodeling in Heart Failure: Current Concepts in Clinical Significance and Assessment". imaging.onlinejacc.org. . See more
Remodeling of the heart is evaluated by performing an echocardiogram. The size and function of the atria and ventricles can be characterized using this test. See moreMany factors influence the time course and extent of remodeling, including the severity of the injury, secondary events (recurrent ischemia . See more
Left ventricular (LV) adverse remodeling is a maladaptive process caused by cardiac injury characterized by morphological changes of LV structure and shape, with subsequent alteration .LV remodeling occurs spontaneously among patients with HCM in several ways: (1) wall thickening, otherwise defined as positive remodeling; (2) wall thinning without impairment of .
dusty baby blue prada
In cardiology, ventricular remodeling (or cardiac remodeling) [1] refers to changes in the size, shape, structure, and function of the heart. This can happen as a result of exercise (physiological remodeling) or after injury to the heart muscle (pathological remodeling). [2]

Left ventricular (LV) adverse remodeling is a maladaptive process caused by cardiac injury characterized by morphological changes of LV structure and shape, with subsequent alteration of the cardiac function [2,3].LV remodeling occurs spontaneously among patients with HCM in several ways: (1) wall thickening, otherwise defined as positive remodeling; (2) wall thinning without impairment of LV systolic function, defined as benign remodeling; (3) a gradual wall thinning process resulting in the loss of LV systolic function or the development of LV . Left ventricular (LV) remodeling after transmural anteroseptal myocardial infarction (MI): 2D echocardiographic evaluation at 1 week and 3 months. Extensive anteroapical akinesis, progressive dilatation, and dysfunction with increased sphericity are evident, as is the development of apical thrombus.
Adverse ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction (MI) is a process of regional and global structural and functional changes in the heart as a consequence of loss of viable myocardium, exuberant inflammatory response, increased wall stress in the border zone and remote myocardium, and neurohormonal activation (Figure 1).
Ventricular remodeling, first described in animal models of left ventricular (LV) stress and injury, occurs progressively in untreated patients after large myocardial infarction and in those with dilated forms of cardiomyopathy.Ventricular remodeling, first described in animal models of left ventricular (LV) stress and injury, occurs progressively in untreated patients after large myocardial infarction and in those with dilated forms of cardiomyopathy.Classification of left ventricular (LV) remodeling according to the temporal pattern is shown, as well as the impact of remodeling on outcomes (survival and heart failure hospitalization). STEMI = ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Left ventricular (LV) remodelling describes the heart’s (mal)adaptation to mechanical, neurohormonal, and inherited changes by regulating ventricular size, shape, and function.Here, we discuss the concepts and clinical implications of cardiac remodeling, and the pathophysiological role of different factors, including cell death, energy metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation, collagen, contractile proteins, calcium transport, geometry and neurohormonal activation.In cardiology, ventricular remodeling (or cardiac remodeling) [1] refers to changes in the size, shape, structure, and function of the heart. This can happen as a result of exercise (physiological remodeling) or after injury to the heart muscle (pathological remodeling). [2]
Left ventricular (LV) adverse remodeling is a maladaptive process caused by cardiac injury characterized by morphological changes of LV structure and shape, with subsequent alteration of the cardiac function [2,3].
LV remodeling occurs spontaneously among patients with HCM in several ways: (1) wall thickening, otherwise defined as positive remodeling; (2) wall thinning without impairment of LV systolic function, defined as benign remodeling; (3) a gradual wall thinning process resulting in the loss of LV systolic function or the development of LV . Left ventricular (LV) remodeling after transmural anteroseptal myocardial infarction (MI): 2D echocardiographic evaluation at 1 week and 3 months. Extensive anteroapical akinesis, progressive dilatation, and dysfunction with increased sphericity are evident, as is the development of apical thrombus.
Adverse ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction (MI) is a process of regional and global structural and functional changes in the heart as a consequence of loss of viable myocardium, exuberant inflammatory response, increased wall stress in the border zone and remote myocardium, and neurohormonal activation (Figure 1). Ventricular remodeling, first described in animal models of left ventricular (LV) stress and injury, occurs progressively in untreated patients after large myocardial infarction and in those with dilated forms of cardiomyopathy.
Ventricular remodeling, first described in animal models of left ventricular (LV) stress and injury, occurs progressively in untreated patients after large myocardial infarction and in those with dilated forms of cardiomyopathy.Classification of left ventricular (LV) remodeling according to the temporal pattern is shown, as well as the impact of remodeling on outcomes (survival and heart failure hospitalization). STEMI = ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction
Left ventricular (LV) remodelling describes the heart’s (mal)adaptation to mechanical, neurohormonal, and inherited changes by regulating ventricular size, shape, and function.
prada 56ms blue
left ventricular remodeling process
drugs that prevent cardiac remodeling
EVERYTHING YOU NEED KNOW ABOUT EVERY 1960s OMEGA SEAMASTER 600 MODELS - WATCH REVIEW 101 - YouTube. Vintage Omega Watches From the 40s to 70s. Seamaster, Jumbo, Bumper, Constellation and.
lv remodelling|concentric remodeling and hyperdynamic systolicfunction