lv overload on ekg | ecg voltage criteria for lvh lv overload on ekg Electrocardiogram. Also called an ECG or EKG, this quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. During an ECG, sensors called electrodes are . FEISOL Elite Tripod CT-3472 M2 Rapid. Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 5 customer ratings. Ungeprüfte Gesamtbewertungen. 629,95 € incl. VAT plus Shipping Costs. Shipping weight: 3.0 kg. In stock. Add to cart. SKU: 851308003060 Categories: RAPID Carbon Tripods, Elite Tripods. Description. Additional information. Reviews (0)
0 · what is lvh on ecg
1 · minimal voltage criteria for lvh
2 · lvh signs on ecg
3 · left ventricular overload ecg
4 · left ventricular hypertrophy on ecg
5 · ecg voltage criteria for lvh
6 · ecg changes in lvh
7 · Lv overload or aspecific change
Each of our high strength, corrosion resistant, specialty fastener products are custom engineered and manufactured from the highest-quality materials to meet your exact specifications. All of our products are melted and manufactured in the United States of America, ensuring quality of material & workmanship and a delivery date you can count on.
what is lvh on ecg
ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common finding in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD risk factors and is diagnosed either by .
Electrocardiogram. Also called an ECG or EKG, this quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. During an ECG, sensors called electrodes are .
Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar .
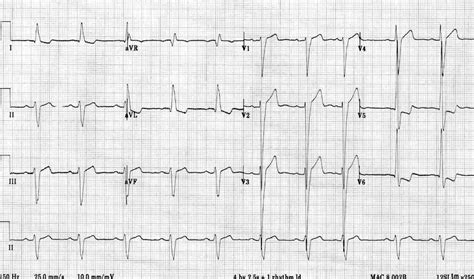
The left ventricle hypertrophies in response to pressure overload secondary to conditions such as aortic stenosis and hypertension. This results in increased R wave amplitude in the left-sided ECG leads (I, aVL and V4-6) and increased S .ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and deep S-waves in right-sided chest leads (V1, V2). Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common finding in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD risk factors and is diagnosed either by electrocardiogram (ECG) or imaging (eg, echocardiography, cardiovascular computed tomography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance [CMR] imaging) [1]. Electrocardiogram. Also called an ECG or EKG, this quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. During an ECG, sensors called electrodes are attached to the chest and sometimes to the arms or legs. Wires connect the sensors to a machine, which displays or prints results.
Criteria for ECG Diagnosis of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. ECG = electrocardiography; LVH = left ventricular hypertrophy. Brought to you by Merck & Co, Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside the US and Canada) — dedicated to using leading-edge science to save and improve lives around the world. Learn more about the MSD Manuals and our . ECG features suggestive of LV dilation (dilated cardiomyopathy) LVH is a bit of a misnomer because this actually reflects increased left ventricular mass (due to increased wall thickness or chamber dilation). The following features may suggest LV chamber dilation: Reduction in R-wave of left precordial leads. Multiple cardiovascular conditions are associated with LVH and cause distinct hypertrophy patterns, myocardial structural alterations, and ECG manifestations. LVH may occur as an adaptation process in response to pressure or volume overload, or be intrinsic (congenital/genetic). A few examples are listed. 4 PATHOLOGY Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis.
The left ventricle hypertrophies in response to pressure overload secondary to conditions such as aortic stenosis and hypertension. This results in increased R wave amplitude in the left-sided ECG leads (I, aVL and V4-6) and increased S .ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and deep S-waves in right-sided chest leads (V1, V2).
minimal voltage criteria for lvh
Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the most common cause of left ventricular hypertrophy. Complications include irregular heart rhythms, called arrhythmias, and heart failure. Treatment of left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. Treatment may include medications or surgery. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common finding in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD risk factors and is diagnosed either by electrocardiogram (ECG) or imaging (eg, echocardiography, cardiovascular computed tomography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance [CMR] imaging) [1]. Electrocardiogram. Also called an ECG or EKG, this quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. During an ECG, sensors called electrodes are attached to the chest and sometimes to the arms or legs. Wires connect the sensors to a machine, which displays or prints results.
Criteria for ECG Diagnosis of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. ECG = electrocardiography; LVH = left ventricular hypertrophy. Brought to you by Merck & Co, Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside the US and Canada) — dedicated to using leading-edge science to save and improve lives around the world. Learn more about the MSD Manuals and our .
ECG features suggestive of LV dilation (dilated cardiomyopathy) LVH is a bit of a misnomer because this actually reflects increased left ventricular mass (due to increased wall thickness or chamber dilation). The following features may suggest LV chamber dilation: Reduction in R-wave of left precordial leads. Multiple cardiovascular conditions are associated with LVH and cause distinct hypertrophy patterns, myocardial structural alterations, and ECG manifestations. LVH may occur as an adaptation process in response to pressure or volume overload, or be intrinsic (congenital/genetic). A few examples are listed. 4 PATHOLOGY

The CT-3372LV M2 Rapid is not only incredibly light and stabile, but also allows for lightning-quick angle adjustment. When no center column is needed, it can be replaced with a standard mount base, effecting even greater weight reduction. The CT-3372LV M2 Rapid is another ground-breaking FEISOL innovation.
lv overload on ekg|ecg voltage criteria for lvh