lv systolic diameter | normal Lv end systolic dimension lv systolic diameter Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium. Jan 22, 2016 at 7:41. Add a comment. A literal answer is this: There are three blown capacitors; two can be seen as spirals of grey material still reasonably in situ, the third is nothing more than the base and the internal terminals. They were all rated for 6.3V but, do to a failure in the power regulator, they were connected to a whopping 7.5V.
0 · normal Lv end systolic dimension
1 · normal Lv end diastolic diameter
2 · left ventricular internal dimension diastole
3 · left ventricular diameter chart
4 · left ventricle size chart
5 · left internal dimension in systole
6 · Lv systolic diameter mm
7 · Lv end diastolic diameter
May 3, 2021. #5. If the manual says Dex/Merc III, then you don't necessarily have to use Mercon V. Typically if an application is rated for Merc V, it is backwards compatible with Dex III, but not always the other way around. You don't mention the vehicle, but Valvoline Maxlife is about the best bang for the buck around and meets both those .
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the .Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.Ejection Fraction (EF) (see below) is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function (see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end .
The LV diameter is a measure that can be easily obtained during echocardiography at the time of LVEF measurement. Previous studies have established the importance of LV size with regard to cardiac mortality.Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no . Learn how to assess LV systolic function using echocardiography, including linear, area, and volume measurements. LV end systolic diameter (LVESD) is one of the parameters used to calculate ejection fraction and .
LV global systolic function is generally assessed by measuring the difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic value divided by the end-diastolic value. This can be applied for either a one-dimensional 2D image or .Measurements of the left ventricle can be obtained by the MMode or by 2D methods. 3.2.2.1.1 MMode measurements / Diameter. MMode still is the most widely used the technique. The reasons are historical. MMode was the first . The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the chordae.Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.
Ejection Fraction (EF) (see below) is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function (see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Global Longitudinal Strain is a new parameter to assess LV systolic function. LV Volumes used to calculate EF The LV diameter is a measure that can be easily obtained during echocardiography at the time of LVEF measurement. Previous studies have established the importance of LV size with regard to cardiac mortality.
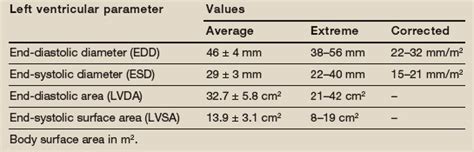
Measures of left ventricular (LV) size obtained in a 36-year-old man, body surface area 2 m 2. LV internal diameter in diastole measured in the normal range (5.6 cm); indexed volume was severely dilated (LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) 200 .Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities.
The measurements required for this quantitative estimate of systolic function are LV internal diameter at end diastole (LVIDd, also called end diastolic diameter LVEDD) and LV internal diameter at end systole (LVIDs, also called end systolic diameter LVESD). LV global systolic function is generally assessed by measuring the difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic value divided by the end-diastolic value. This can be applied for either a one-dimensional 2D image or in 3D.Measurements of the left ventricle can be obtained by the MMode or by 2D methods. 3.2.2.1.1 MMode measurements / Diameter. MMode still is the most widely used the technique. The reasons are historical. MMode was the first technique of echocardiography.
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the chordae.
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.Ejection Fraction (EF) (see below) is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function (see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Global Longitudinal Strain is a new parameter to assess LV systolic function. LV Volumes used to calculate EF
The LV diameter is a measure that can be easily obtained during echocardiography at the time of LVEF measurement. Previous studies have established the importance of LV size with regard to cardiac mortality.
Measures of left ventricular (LV) size obtained in a 36-year-old man, body surface area 2 m 2. LV internal diameter in diastole measured in the normal range (5.6 cm); indexed volume was severely dilated (LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) 200 .Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities.
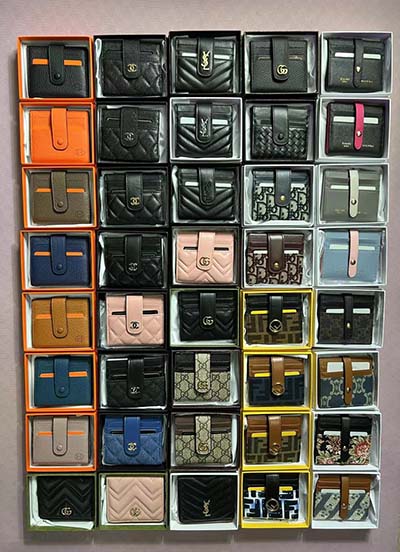
versace slipper replica
The measurements required for this quantitative estimate of systolic function are LV internal diameter at end diastole (LVIDd, also called end diastolic diameter LVEDD) and LV internal diameter at end systole (LVIDs, also called end systolic diameter LVESD). LV global systolic function is generally assessed by measuring the difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic value divided by the end-diastolic value. This can be applied for either a one-dimensional 2D image or in 3D.
normal Lv end systolic dimension
normal Lv end diastolic diameter
Ēters ir viela, līdzīga gaisam kas piepilda visu vakuumu ar ļoti mazām daļiņām un līdz relativitātes teorijas laikam visi zinātnieki uzskatīja to par absolūti pareizu.Savukārt Einšteins ar savu relativitātes teoriju uzstājās pret ētera teoriju, līdzarto tā pamazām tika atmesta, tomēr tas radīja ļoti būtiskas problēmas .
lv systolic diameter|normal Lv end systolic dimension