lv esv index | esv vs edv lv esv index The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) . CoverMe - Sūdzības un atsauksmes. CoverMe - Skilta prece. Nopirku telefona aizsargstiklu, kurš izmaksāja 20€, bet jau pirmajā dienā tas ieplīsa, ne no kā, vienkārši vienā brīdī izvelkot telefonu no kabatas, sapratu, ka tas ir ieplīsis. Kabatā nebija nekas cits, tikai telefons.
0 · lvef vs edv
1 · esvi x ray
2 · esvi blood test
3 · esv vs edv normal range
4 · esv vs edv
5 · esv stroke volume chart
6 · esv normal range chart
7 · esv mri normal range
In the study, reported by Guzik et al. in this issue, 9 patients with concentric LVH had more adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events and higher mortality than in those with eccentric LVH, thus suggesting that the geometric category of LVH may impact the long-term prognosis in patients with hypertension.
goyard 通販
lvef vs edv
The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) .Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and LV mass (LVM) were 11.9 ± 5.6% and 20.2 ± 4.3%, respectively, significantly affecting.
esvi x ray
The end-systolic volume index (ESVI) is the end-systolic volume corrected for the body surface area (BSA). Usage. In addition to the end-diastolic volume, the end-systolic volume is an essential parameter used for the assessment of cardiac function and the calculation of the respective stroke volumes and ejection fraction. Measurement. MRI.
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
The left atrial end-systolic volume index (LAESVI), representing the largest left atrial (LA) volume, is a known predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and is the recommended measure of LA size by the American Society of Echocardiography. 1 The LA residual volume index or the LA end-diastolic volume index (LAEDVI) is the smallest LA volume .End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole. ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle.
Objective: Left ventricular (LV) end-systolic volume indexed to body surface area (ESVI) is a simple yet powerful echocardiographic marker of LV remodeling that can be measured easily.Assessment of left ventricular (LV) function is critical for clinical decision-making in patients with valvular heart disease. 1 Patients with hemodynamically significant aortic regurgitation (AR) incur excess mortality. 2 Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)–derived prognostic indexes 1 in AR are based on LV linear measurements, including . Left ventricular (LV) end-systolic volume indexed to body surface area (ESVI) is a simple yet powerful echocardiographic marker of LV remodeling that can be measured easily. The prognostic value of ESVI and its merit relative to other markers of LV remodeling in patients with coronary heart disease are unknown.Six clinical indices were chosen and ranked based on their variance in the population: End-Diastolic Volume Index (EDVI), which is end-diastolic volume (EDV) divided by body surface area. Sphericity = EDV divided by the volume of a sphere with a diameter corresponding to the major axis at ED in LV long-axis view.
The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and LV mass (LVM) were 11.9 ± 5.6% and 20.2 ± 4.3%, respectively, significantly affecting. The end-systolic volume index (ESVI) is the end-systolic volume corrected for the body surface area (BSA). Usage. In addition to the end-diastolic volume, the end-systolic volume is an essential parameter used for the assessment of cardiac function and the calculation of the respective stroke volumes and ejection fraction. Measurement. MRI.Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
The left atrial end-systolic volume index (LAESVI), representing the largest left atrial (LA) volume, is a known predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and is the recommended measure of LA size by the American Society of Echocardiography. 1 The LA residual volume index or the LA end-diastolic volume index (LAEDVI) is the smallest LA volume .End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole. ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle.Objective: Left ventricular (LV) end-systolic volume indexed to body surface area (ESVI) is a simple yet powerful echocardiographic marker of LV remodeling that can be measured easily.Assessment of left ventricular (LV) function is critical for clinical decision-making in patients with valvular heart disease. 1 Patients with hemodynamically significant aortic regurgitation (AR) incur excess mortality. 2 Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)–derived prognostic indexes 1 in AR are based on LV linear measurements, including .
Left ventricular (LV) end-systolic volume indexed to body surface area (ESVI) is a simple yet powerful echocardiographic marker of LV remodeling that can be measured easily. The prognostic value of ESVI and its merit relative to other markers of LV remodeling in patients with coronary heart disease are unknown.
esvi blood test
esv vs edv normal range
goyard volataire
goyard st sulpice replica
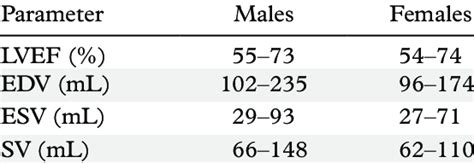
chocardiographic evaluation of wall motion (WM) is a simple, well-validated method to assess segmental left ventricular (LV) function.1,2 The presence of qualitative WM abnormalities has been demonstrated to be an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in groups of patients with myocardial infarction (MI),3,4 unstable angina,5 typical .
lv esv index|esv vs edv